
ELECTROMAGNETISM
Magnetic Induction, Inductance, AC and LC Circuits
Assessment
This part of the module suggests assessment on the topics covered in the content discussion. The end-user of the module may create his/her own assessment dependent on the achievement of the students based on the learning competencies stated at the start of the module.
I. TRUE OR FALSE:
_______1. Constant magnetic field produces current.
_______2. Moving charges in a coil can induce magnetic field.
_______3. The higher the number of coils, the lesser the magnetic field induced.
_______4. The faster the speed of the magnet inside the coil of wire, the greater the magnetic field induced.
_______5. Magnetic flux is maximum when the angle between the magnetic field and the normal is 90 degrees .
_______6. The strength of an electromagnet depends on the number of coils, length of the wire and the amount of current present.
_______7. Electromagnets can lift large metal objects containing iron.
_______8. Current is induced when a coil moves with the same velocity as the magnet.
II. SHORT RESPONSE
-
Whenever there is lightning nearby, electrical appliances inside the house must be turned off. Why is this precaution taken? Explain using the principle of electromagnetic induction._______________________________________________________________________________________________
-
How does electromagnet lift a train and make it levitate?
___________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
3. There was a gameshow that was popularized by a TV station where the
contestants have to succesfully crossover a coil of wire looped around a
circuit which is connected to a light bulb. Everytime a contestant touches
the circuit,the bulb will light or buzzer will beep and he/she is automatically
disqualified from the game. Explain why there is a slim chance for a
contestant to win in this contest.
___________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
III. DIAGRAM ANALYSIS
A ring is dropped into a region of constant magnetic field directed perpendicular into the page. What is the direction of induced current on each phase of the ring falling?
-
Position A ____________
-
Position B ____________
-
Position C ____________
-
Position D ____________
-
Position E ____________
IV. PROBLEM SOLVING
V. COMPARE AND CONTRAST
Fill-in the missing properties for Alternating and Direct Currents.
VI. PROBLEM SOLVING on LC Circuit
A .50 F capacitor is charged to 10V and then is attached to a 3 H inductor.
a) Find the frequency of the circuit’s oscillation?
b) Find the charge of the capacitor and current of the inductor at t=3.5s.
c) Find the energy stored in the circuit.

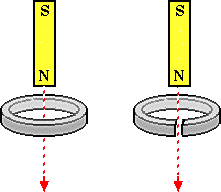
A magnet moves through a coil directed downward as shown.
6. What is the direction of the induced current as it enters the ring?__________
7. How about as the magnet moves away from the ring?_____________________
8. What happens to the induced current when the ring is broken as shown on the right?____________________________
A coil of wire is oriented so that the normal to its surface is parallel to a constant magnetic field of 0.17 T. The coil is then rotated through an angle of 30˚ in a time of 0.10 s.
a) Determine the average induced emf if the coil has an area of 0.030 m*2 and 40 turns of wire
b) What would be the induced emf if the coil were returned to its original orientation in the same time of 0.10 s?

SUGGESTED ANSWER
I. TRUE OR FALSE
1. False
2.True
3. False
4.True
5.False
6.True
7.True
8.False
II. SHORT RESPONSE
1. When lightning strikes in a nearby area, the changing current can induce magnetic field in the coils of wire of appliances which can in turn induce current on these appliances, so the danger of additional current can make the appliances burn or explode.
2. The train's railway is composed of electromagnet. When current is turned on, the train's railway will repel with the electromagnet attached on the train itself. This will cause the train to levitate above its track.
3. Aside from the fact that it could be tiring for the hand, as the coil moves over the loop of wire, magnetic field is induce which will increase the chance of touching the wire.
III. DIAGRAM ANALYSIS
1. no current induced since no magnetic field present
2. counterclockwise using RHR
3. no current induced because of uniform magnetic field
4.clockwise
5.no current induced
6. counterclockwise, since the coil will set up a magnetic field that has a North-South orientation to counteract the increasing flux.
7.clockwise, coil will set-up a field to attract the outgoing flux
8.no current is induced
IV. PROBLEM SOLVING
1.0.27 V
2.-0.27 V
V. COMPARE AND CONTRAST
(a) Amount of energy that can be carried - Safe to transfer over longer city distances and can provide more power.
(b) Cause of the direction of flow of electrons - Rotating magnet along the wire.
(c) Frequency - The frequency of direct current is zero.
(d) Direction - It reverses its direction while flowing in a circuit.
(e) Current - It is the current of magnitude varying with time.
(f) Flow of Electrons - Electrons move steadily in one direction or 'forward'.
(g) Obtained from - A.C Generator and mains.
VI. PROBLEM SOLVING on LC Circuit
NOTE:
This assessment may come as a unit test (summative) since there are formative assessments included in the content discussion.
